
Diffusion-tensor MRI and tractography may offer radiologists a noninvasive option for diagnosing esophageal carcinoma.

Diffusion-tensor MRI and tractography may offer radiologists a noninvasive option for diagnosing esophageal carcinoma.

Calgary Scientific’s ResolutionMD received FDA clearance for diagnosis on mobile devices for most imaging modalities.

Imaging with CT and coronary CT angiography shows prevalent and extensive presence of coronary artery plaque among men infected with HIV.

Dual-energy CT may help clinicians diagnose gout when MSU crystals are not observed through polarizing microscopy.

The use of PET imaging in non-small cell lung cancer patients reduced the number of unnecessary surgeries by 50 percent.
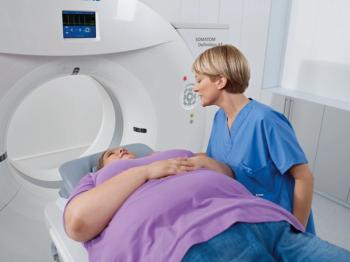
When it comes to working with obese patients, manufacturers and clinicians are trying to solve the challenges presented in diagnostic imaging.

The latest KLAS report shows that providers who chose the more cost-effective options for CT scanners are happy with the products.

Use of nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging exams dropped sharply between 2006 and 2011, but substitute imaging studies haven’t increased.

Could PET/MR be a better modality than conventional MR and CT for bladder cancer?
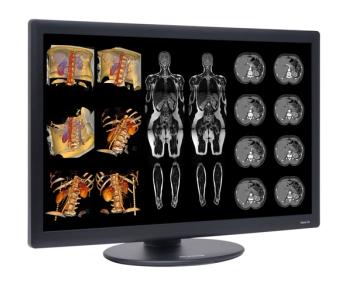
The FDA has given clearance to NDS Surgical Imaging for the Dome S6c diagnostic display.

Physicians and radiologists should clearly communicate risks and benefits of imaging procedures, especially for pediatric patients.

The FDA approved Neuraceq for PET imaging of the brain to identify beta-amyloid neuritic plaque in patients with cognitive decline or Alzheimer’s disease.

Magnetic resonance imaging is an effective alternative to ultrasounds and CT scans in diagnosing pediatric appendicitis.

Clinical decision support tools can help standardize best practices for radiologists and patients.
Check out some of the technological advances in radiology monitors.

Unnecessary brain scans for complaints of headache and migraine becoming more popular, but are costly for the health care system.

Using NaF-PET to evaluate prostate cancer progression and evidence of osseous metastases allows clinicians to change treatment plans.
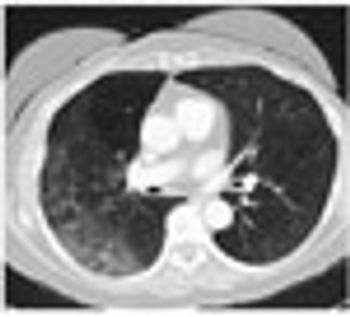
Medicare should fully cover low-dose CT lung cancer screening as per the USPSTF recommendations for high-risk patients.
Study provides no additional evidence supporting 2008 FDA advisory that warned CT scans potentially interfere with CRM devices.

Low-dose CT community-based lung cancer screening program effective and feasible.

More radiology tests found to be of low-value in the emergency room.

Use of CTs for the spine growing, despite slowing down of overall CT imaging.

Adrenal tumors that are detected incidentally by CT scan should be followed up due to an increased risk of cardiovascular events caused by increased tumor activity.

CT angiography and SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging improves with the use of synchronized multimodal heart visualization software.

Using CT to measure coronary artery calcium may aid physicians in predicting the chances of incident cardiovascular events.