
Computed tomography and MRI may not be necessary for most patients who present to the emergency department with acute pancreatitis.

Computed tomography and MRI may not be necessary for most patients who present to the emergency department with acute pancreatitis.

Case History: 10-year-old male child presents with six-month history of difficulty opening mouth.

Non-enhanced CT scans for suspected renal colic often detect incidental findings.

Advanced imaging may not be necessary for many people with headaches, but clinicians are ordering them for their patients.

Case History: 36-year-old Asian male presented with complaints of a first episode of generalized tonic-clonic convulsions

Dose for CT examination of children can be calculated by the children’s weight rather than torso diameter measurement.

Despite recommendations not to perform imaging for patients with peripheral vertigo, up to one-fifth of patients had a head CT while in the ED.
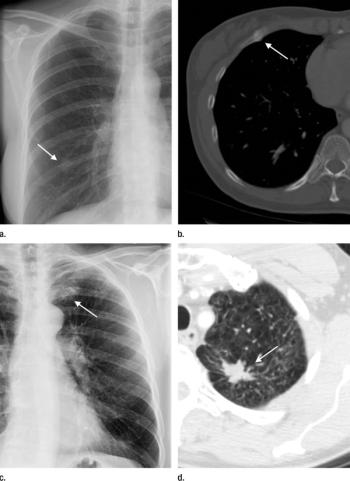
Chest CT follow-ups recommended by radiologists following chest radiograph result in clinically relevant findings.

Case History: 40-year-old patient with one-week history of seizure and altered sensorium.

Using a structured order entry for trauma CTs results in better communication, recording, and billing.

CT images help identify patients who may have a subsequent stroke within three months of experiencing a TIA.

When general clinicians were educated about and given access to low-dose computed tomography, more lung cancers were diagnosed.

Pelvic CT with filtered back projection and 50% ASIR reduces dose.

Lung cancer screening based on PLCOm2012 model criteria is more effective than the USPSTF criteria.

Imaging detects pituitary abnormalities in military veterans who have both mild traumatic brain disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder.

GE to showcase at RSNA 2014 its Revolution family of CT scanners.

Vendors reveal what products they are most excited about showcasing at RSNA 2014.

Imaging for patients with Ebola virus is necessary, but new protocols need to be established to prevent spread of the disease.

44-year-old male with a history of absence seizures, migraines, peripheral neuropathy, and multisystem sarcoidosis.

Case History: 82-year-old male presented with acute onset of right inguinal region mass.

Routine CT angiography for patients with diabetes not more effective in preventing cardiovascular complications than good standard of care.

Attempts at determining imaging efficiency identifies hospitals with inefficient practices but not hospitals that are doing well.

Coverage of low-dose CT for lung cancer screening makes for an historical lung cancer awareness month.

With the advancement of medical imaging technology comes the need for updated safeguards.
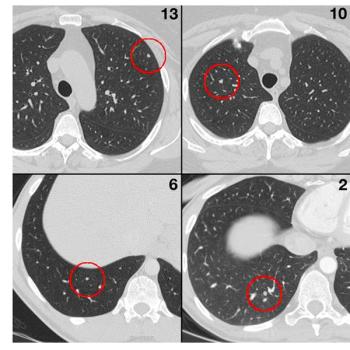
Radiologists tend to focus on certain areas of lung CT images, which could result in missed nodules.