Oncology CT
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
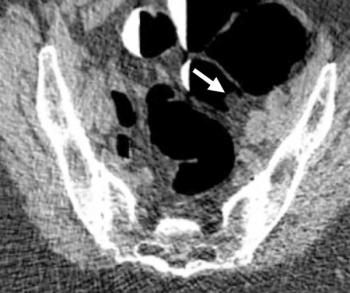
Computed tomography colonography (CTC) demonstrated a 91.6 percent positive predictive value (PPV) for polyps > 6 mm, according to new research involving over 9,000 patients who underwent CTC for primary asymptomatic colorectal cancer screening.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
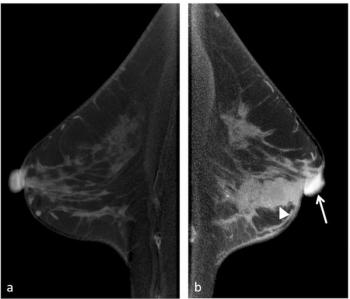
Preoperative use of contrast-enhanced cone-beam breast CT has over a 96 percent sensitivity for predicting nipple-areolar complex involvement in cases involving early-stage breast cancer, according to a new study.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
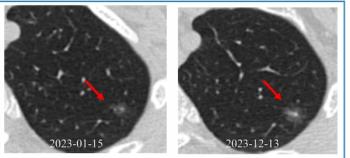
Emerging research shows that a multiple time-series deep learning model assessment of CT images provides 20 percent higher sensitivity than a delta radiomic model and 56 percent higher sensitivity than a clinical model for prognostic evaluation of ground-glass nodules.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
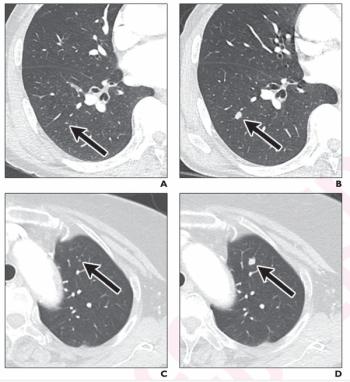
Researchers also noted a greater than 30 percent increase in treatment management changes resulting from the use of CT-based adjunctive AI to detect lung metastases in colorectal cancer patients.
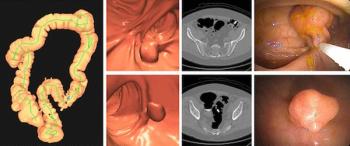
Emerging research suggests the use of computed tomography colonography (CTC) in colorectal cancer screening may provide significantly higher preventive benefit at lower costs in comparison to multitarget stool DNA testing.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in May 2025.
In a review of 155 studies, researchers examined the capabilities of photon-counting computed tomography (PCCT) for enhanced accuracy, tissue characterization, artifact reduction and reduced radiation dosing across thoracic, abdominal, and cardiothoracic imaging applications.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
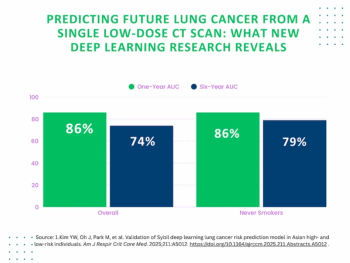
In never-smokers, deep learning assessment of single baseline low-dose computed tomography (CT) scans demonstrated a 79 percent AUC for predicting lung cancer up to six years later, according to new research presented today at the American Thoracic Society (ATS) 2025 International Conference.
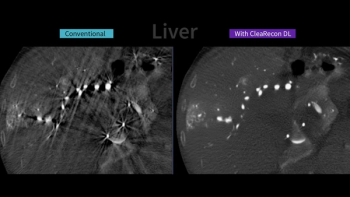
The CleaRecon DL software reportedly removes streak artifacts that can occur with the use of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) during interventional radiology procedures.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
In comparison to American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM staging, an emerging CT-based scoring system for assessing early recurrence of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma demonstrated over a 22 percent higher AUC in testing and external validation cohorts in a new study.
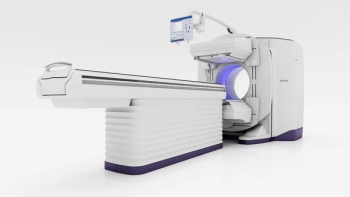
The combination of the Aurora SPECT/CT system with AI-enabled Clarify DL image reconstruction reportedly offers the potential of enhanced image quality and streamlined workflows in nuclear medicine.

In a second part of a new podcast episode on recently published research on projected radiation-induced cancers from computed tomography (CT) scans, Mahadevappa Mahesh, MS, Ph.D., and Joseph Cavallo, M.D., offer current perspectives on cardiac CT dosing, AI advances and the importance of teamwork in ensuring appropriate dosing for CT.

In a new podcast, Mahadevappa Mahesh, MS, Ph.D., and Joseph Cavallo, M.D., share their perspectives on recently published research looking at projections for future radiation-induced cancers from computed tomography (CT) scans.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in April 2025.

Catch up on the most well-viewed video interviews from Diagnostic Imaging in April 2025.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
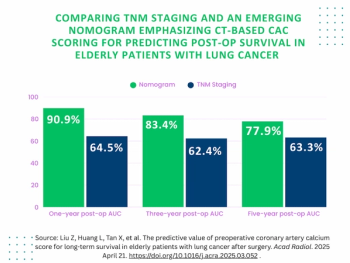
For elderly patients with lung cancer, a preoperative CT-based coronary artery calcium score > 40 was associated with a 53 percent higher risk of all-cause mortality after surgery, according to new study findings.

In a recent interview, Syam Reddy, M.D., discussed the rising incidence of colon cancer and a clinical pathway resource with Radiology Partners that facilitates the integration of computed tomography colonography (CTC) into radiology practice.