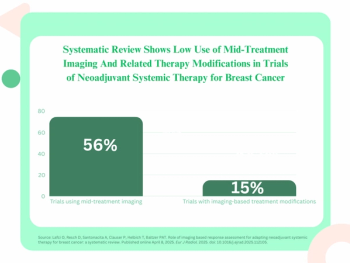
A systematic review of 147 clinical trials assessing neoadjuvant systemic therapy for breast cancer also revealed that mid-treatment imaging was utilized in 56 percent of the studies.

A systematic review of 147 clinical trials assessing neoadjuvant systemic therapy for breast cancer also revealed that mid-treatment imaging was utilized in 56 percent of the studies.
Going into effect in 2026, the new CPT codes may facilitate increased adoption of the CaRi-Heart software for detecting coronary inflammation from computed tomography scans pending FDA clearance of the technology.
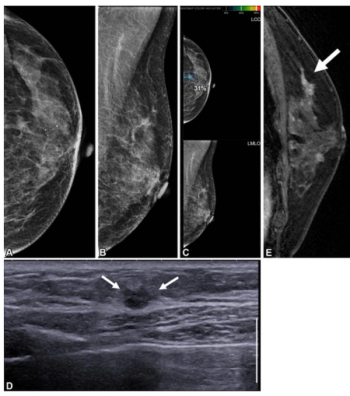
While standalone AI interpretation offered over 10 percent higher sensitivity than radiologists for patients undergoing post-mastectomy surveillance mammography, it missed over 30 percent of breast cancers.

For patients with acute ischemic stroke, research has demonstrated that automated assessment of ischemic core volume on brain CT scans via the Brainomix 360 software is equivalent to that derived from CT perfusion.

Emerging research from the recent Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR) conference suggests the combination of transarterial radioembolization (TARE) and immunotherapy may offer improved three-year survival outcomes for patients with breast cancer and liver metastases.
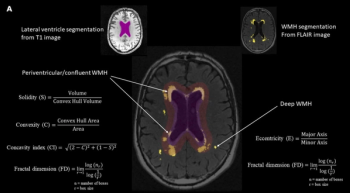
Emerging research demonstrated that cognitive declines in memory, executive function and processing speed domains were associated with irregular shape of periventricular/confluent white matter hyperintensities.

While the best-laid plans may become fraught with contingencies and detours, how we react to them changes with the wisdom of experience.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
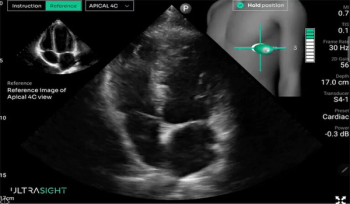
In a study recently presented at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) conference, researchers found that novice use of AI-guided cardiac ultrasound after an AI-enabled electrocardiogram increased the positive predictive value for reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) or aortic valve stenosis by 33 percent.
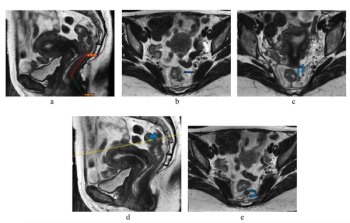
Abbreviated MRI demonstrated a 95.3 percent specificity for rectal cancer and provided strong agreement with the full MRI protocol for T staging and detection of extramural venous invasion, according to newly published research.
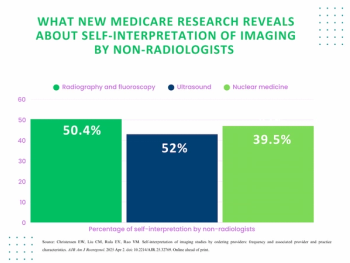
In a review of over 1,630,000 office-based non-breast imaging Medicare fee-for-service (FFS) claims from 2022, researchers found that 39.5 percent of nuclear medicine imaging were interpreted by ordering clinicians.
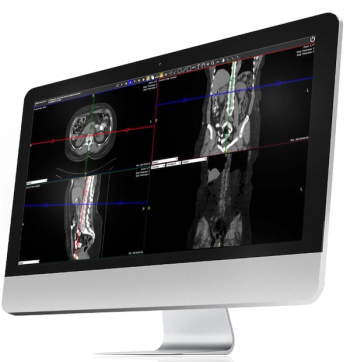
The Exa PACS/RIS platform reportedly combines AI-enabled worklist navigation tools with advances in multiplanar functionality and 3D-generated image segmentation.
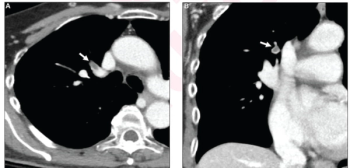
After a multivariable assessment including age and comorbidities, women with pulmonary embolism (PE) had a 48 percent higher risk of one-year mortality than men with PE, according to a new study involving over 33,000 patients.
Featuring enhanced low-dose image quality with motion-free images, the Revolution Vibe CT system reportedly facilitates improved diagnostic clarity for patients with conditions ranging from in-stent restenosis to atrial fibrillation.
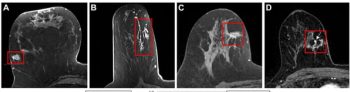
New multicenter research suggests that radiomic features derived from breast MRI may enhance prognostic capabilities with disease upstaging for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS).
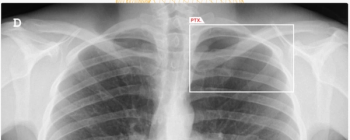
The AI-powered AZchest CXR software reportedly offers 93.79 percent sensitivity and a 98.57 percent AUC for pneumothorax.
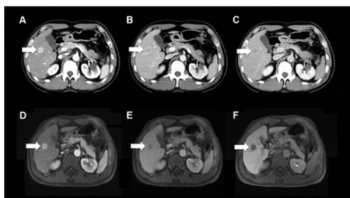
LI-RADS category 5 (LR-5) assessment had an 11 percent higher AUC for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients with non-cirrhotic chronic hepatitis C (CHC) in comparison to those with cirrhotic CHC.
How should you respond when being thanked broadly for the work you do in radiology?
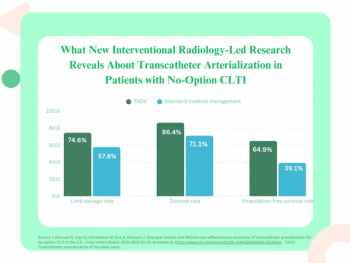
For patients with no-option chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI), transcatheter arterialization provided over a 25 percent higher amputation-free survival rate over standard medical management at one year, according to research presented at the Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR) Annual Scientific Meeting.

Catch up on the top radiology content of the past week.
Recent research demonstrated a 59 percent reduced risk of progression or death with the radioligand therapy Pluvicto in comparison to a change of androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI) for patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC).
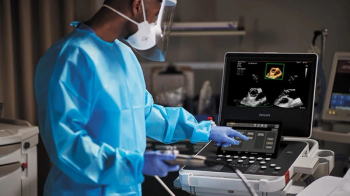
Artificial intelligence (AI)-powered measurement capabilities provide key features with the Compact Ultrasound 5500CV device, which was unveiled at the American College of Cardiology (ACC) conference.
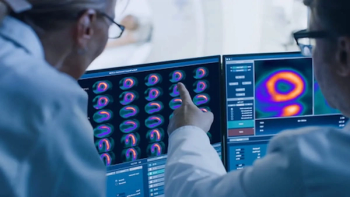
The positron emission tomography myocardial perfusion imaging (PET MPI) agent, which offers a significantly higher half-life than other cardiac PET agents, was recently granted pass-through payment status by CMS that will go into effect on April 1, 2025.
Catch up on the most-well viewed radiology content in March 2025.

Catch up on the most-well viewed prostate imaging content in March 2025.
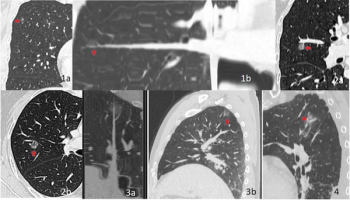
The cLung-RADS v2022 model offered a greater than 16 percent increase in the AUC in comparison to Lung-RADS 1.0 and Lung-RADS v2022 systems for predicting the invasiveness of pure ground-glass nodules.
In addition to a variety of tools to promote radiology workflow efficiencies, the integration of the Gravity AI tools into the PowerServer RIS platform may reduce time-consuming prior authorizations to minutes for completion.

Catch up on the top AI-related news and research in radiology over the past month.
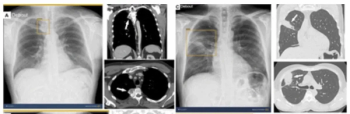
Adjunctive use of the AI-powered software led to an average 38.6 percent increase in the detection of pneumothorax by general radiologists, according to a 2023 study.
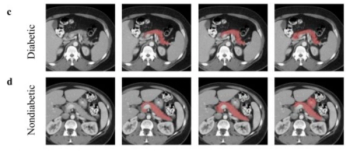
Attenuation-based biomarkers on computed tomography (CT) scans demonstrated a 93 percent interclass correlation coefficient (ICC) agreement across three pancreatic segmentation algorithms for predicting diabetes, according to a study involving over 9,700 patients.